"The journey of a thousand miles begins with a single objective written."
Writing learning objectives is always a daunting start, yet motivational, the initial step of commitment to self-improvement.
If you are looking for a good way to write a learning objective, we've got your cover. This article provides you with the best learning objectives examples and tips on how to write them effectively.
| What are the 5 learning objectives? | Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Timely. |
| What are the 3 purposes of learning objectives? | Set a goal, guide the learning, and help learners concentrate on their process. |
Table of Contents:
- What are learning objectives?
- What makes good learning objectives examples?
- Good Learning Objectives Examples
- Tips to write well-defined learning objectives
- Frequently Asked Questions
What are Learning Objectives?
On one hand, learning objectives for courses are often developed by educators, instructional designers, or curriculum developers. They outline the specific skills, knowledge, or competencies that students should acquire by the end of the course. These objectives guide the design of the curriculum, instructional materials, assessments, and activities. They provide a clear roadmap for both the instructors and the students about what to expect and what to achieve.
On the other hand, learners also can write their own learning objectives as self-study. These objectives can be broader and more flexible than course objectives. They might be based on the learner's interests, career aspirations, or areas they wish to improve. The learning objectives might include a mix of short-term goals (e.g., completing a specific book or online course) and long-term goals (e.g., mastering a new skill or becoming proficient in a certain field).
What Makes Good Learning Objectives Examples?

The key to writing effective learning objectives is to make them SMART: Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Timely.
Here’s an example of SMART learning objectives for your skill courses through SMART goal setting: By the end of the course, I will be capable of planning and implementing a basic digital marketing campaign for a small business, effectively using social media and email marketing.
- Specific: Learn the fundamentals of social media and email marketing
- Measurable: Learn how to read metrics such as engagement rates, click-through rates, and conversion rates.
- Achievable: Apply strategies learned in the course to a real scenario.
- Relevant: Analyzing data helps refine marketing strategies for better outcomes.
- Time-bound: Achieve the goal in three months.
Good Learning Objectives Examples
When writing learning objectives, it's important to use clear and action-oriented language to describe what learners will be able to do or demonstrate after completing a learning experience.
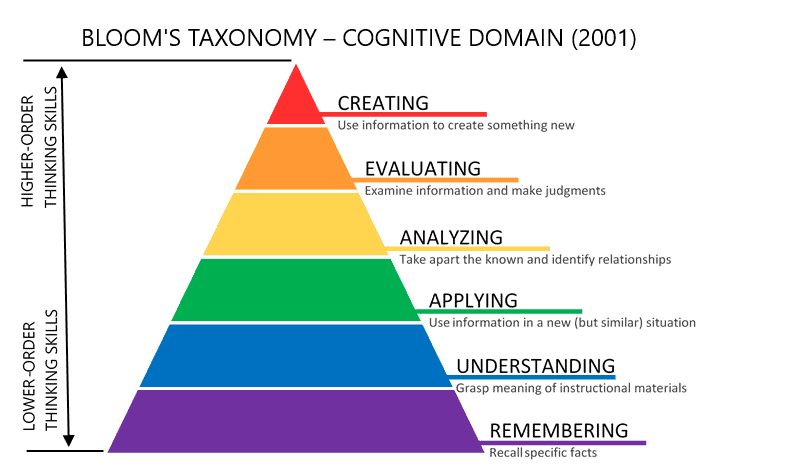
Benjamin Bloom created a taxonomy of measurable verbs to help us describe and classify observable knowledge, skills, attitudes, behaviors, and abilities. They can be used in the different levels of thinking, including Knowledge, Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Synthesis, and Evaluation.
Common Learning Objectives Examples
- After reading this chapter, the student should be able to [....]
- By the end of [....], students will be able to [....]
- After a lesson on [....], students will be able to [....]
- After reading this chapter, the student should understand [....]
Learning Objectives Examples on Knowledge
- Understand the significance of / the importance of [....]
- Understand how [.....] differ from and similar to [....]
- Understand why [.....] has a practical influence on [....]
- How to plan for [....]
- The frameworks and patterns of [....]
- The nature and logic of [....]
- The factor that influences [....]
- Participate in group discussions to contribute insights on [....]
- Derive [....]
- Understand the difficulty of [....]
- State the reason for [....]
- Underline [....]
- Find the meaning of [....]

Learning Objectives Examples on Comprehension
- Identify and explain [....]
- Discuss [....]
- Identify the ethical issues related to [....]
- Define / Identify / Explain / Compute [....]
- Explain the difference between [....]
- Compare and contrast the differences between [....]
- When [....] are most useful
- The three perspectives from which [....]
- The influence of [....] on [....]
- The concept of [....]
- The basic stages of [....]
- The major descriptors of [....]
- The major types of [....]
- Students will be able to accurately describe their observations in [....]
- The use and the difference between [....]
- By working in collaborative groups of [....], students will be able to form predictions about [....]
- Describe [....] and explain [....]
- Explain the issues related to [....]
- Classify [....] and give a detailed classification of [....]
Learning Objectives Examples on Application
- Apply their knowledge of [....] in [....]
- Apply the principles of [....] to solve [....]
- Demonstrate how to use [....] to [....]
- Solve [....] using [....] to reach a viable solution.
- Devise a [....] to overcome [....] by [....]
- Cooperate with team members to create a collaborative [....] that addresses [....]
- Illustrate the use of [....]
- How to interpret [....]
- Practice [....]
Learning Objectives Examples on Analysis
- Analyze the factors contributing to [....]
- Analyze the strengths of / the weaknesses of [....] in [....]
- Examine the relationship that exists between [....] / The link forged between [....] and [....] / The distinctions between [....] and [....]
- Analyze the factors contributing to [....]
- Students will be able to categorize [....]
- Discuss the supervision of [....] in terms of [....]
- Break down [...]
- Differentiate [....] and identify [....]
- Explore the implications of [....]
- Investigate the correlations between [....] and [....]
- Compare / Contrast [...]
Learning Objectives Examples on Synthesis
- Combine insights from various research papers to construct [....]
- Design a [....] that meets [....]
- Develop a [plan/strategy] to address [....] by [....]
- Construct a [model/framework] that represents [....]
- Integrate principles from different scientific disciplines to propose [....]
- Integrate concepts from [multiple disciplines/fields] to create a cohesive [solution/model/framework] for addressing [complex problem/issue]
- Compile and organize [various perspectives/opinions] on [controversial topic/issue] to [....]
- Combine elements of [....] with established principles to design a unique [....] that addresses [....]
- Formulate [...]
Learning Objectives Examples on Evaluation
- Judge the effectiveness of [....] in achieving [....]
- Assess the validity of [argument/theory] by examining [....]
- Critique the [....] based on [....] and provide suggestions for improvement.
- Evaluate the strengths of / the weaknesses of [....] in [....]
- Evaluate the credibility of [....] and determine its relevance to [....]
- Appraise the impact of [....] on [individuals/organization/society] and recommend [....]
- Measure the impact of / the influence of [....]
- Compare the benefits and drawbacks of [....]
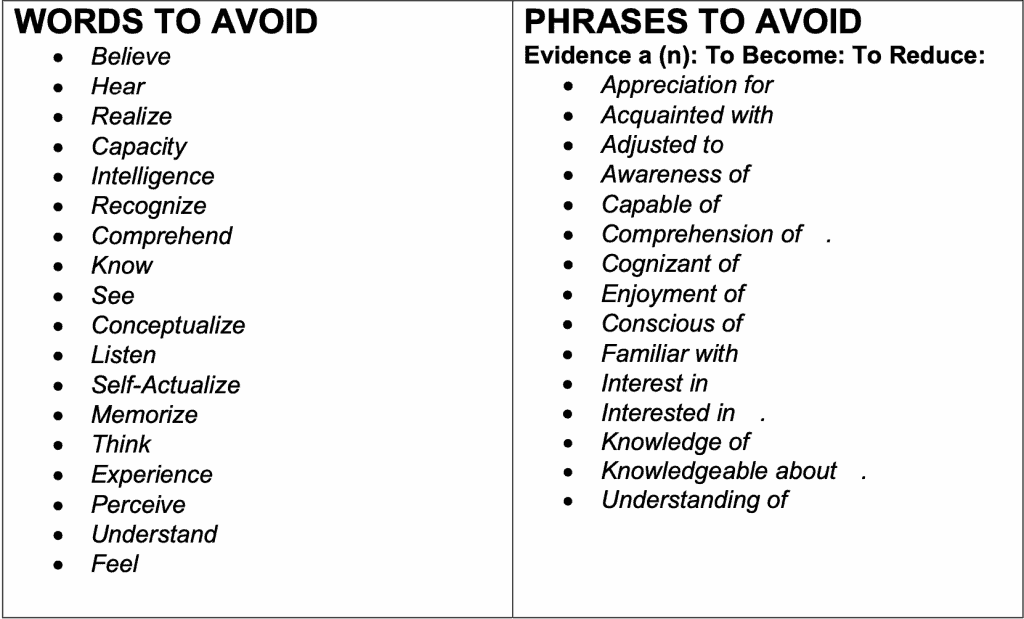
Tips to write well-defined learning objectives
To create well-defined learning objectives, you should consider applying these tips:
- Align with the identified gaps
- Keep statements brief, clear, and specific.
- Follow a student-centered format versus a faculty- or instruction-centered format.
- Use measurable verbs from Bloom’s Taxonomy (Avoid vague verbs like know, appreciate,...)
- Include only one action or outcome
- Embrace the Kern and Thomas Approach:
- Who = Identify the audience, for example: The participant, learner, provider, physician, etc...
- Will do = What do you want them to do? Illustrate the anticipated, observable action/behavior.
- How much (how well) = How well should the action/behavior be done? (if applicable)
- Of what = What do you want them to learn? Demonstrate the knowledge that should be acquired.
- By when = End of the lesson, chapter, course, etc.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the four types of learning objectives?
Before looking at objective learning examples, it is important to understand a classification of learning objectives, which gives you a clearer picture of how your learning goals should be.
Cognitive: be congruent with knowledge and mental skills.
Psychomotor: be congruent with physical motor skills.
Affective: be congruent with feelings and attitudes.
Interpersonal/Social: be congruent with interactions with others and social skills.
How many learning objectives should a lesson plan have?
It is important to have 2-3 objectives in a lesson plan at least for high school level, and an average is up to 10 objectives for higher education courses. This helps educators scaffold their teaching and assessment strategies to promote higher-order thinking skills and a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
What is the difference between learning outcomes and learning objectives?
A learning outcome is a broader term that describes the overall purpose or goal of learners and what they will be capable of achieving once they have completed a program or course of study.
In meanwhile, learning objectives are more specific, measurable statements that describe what a learner is expected to know, understand, or be able to do after completing a lesson or a study program.
Ref: your dictionary | study | utica | facs








