Chan e dìreach faclan-faire eireachdail a th’ ann an dòighean teagaisg ùr-ghnàthach—tha iad nan innealan riatanach airson seòmraichean-teagaisg a chruthachadh far am bi oileanaich dha-rìribh… ag iarraidh airson ionnsachadh. Ge bith a bheil thu a’ teagasg ann an seòmar-teagaisg traidiseanta, air-loidhne, no ann an àrainneachd measgaichte, faodaidh na dòighean-obrach seo ath-bhualadh a thoirt air mar a bhios na h-oileanaich agad an sàs ann an susbaint agus sgilean deatamach a leasachadh airson an ama ri teachd. Feuchaidh sinn ris na dòighean seo a sgrùdadh agus molaidhean gus an cuideachadh le na h-oileanaich agad gu h-ìosal.
Clàr-innse
- 15 Dòighean Teagaisg Ùr-ghnàthach
- 1. Leasanan eadar-ghnìomhach
- 2. A 'cleachdadh teicneòlas virtual reality
- 3. A 'cleachdadh AI ann am foghlam
- 4. Ionnsachadh coimeasgaichte
- 5. Clò-bhualadh 3D
- 6. Cleachd am pròiseas dealbhaidh-smaoineachaidh
- 7. Ionnsachadh stèidhichte air pròiseact
- 8. Ionnsachadh stèidhichte air rannsachadh
- 9. Measg
- 10. Ionnsachadh air a stiùireadh le rannsachadh
- 11. Flipped clas
- 12. Teagasg Chomhaoisean
- 13. Teagasg atharrachail le anailitigeachd ionnsachaidh
- 14. Teagasg crossover
- 15. Ionnsachadh pearsanaichte
- Ceistean Bitheanta
Dè a th’ ann an Dòighean Teagaisg Ùr-ghnàthach?
Chan eil dòighean teagaisg ùr-ghnàthach dìreach mu bhith a’ cleachdadh an teicneòlais as ùire sa chlas no a’ cumail suas ris na gluasadan foghlaim as ùire.
Tha iad uile mu dheidhinn a bhith a’ cleachdadh ro-innleachdan teagaisg ùra a chuireas fòcas nas motha air oileanaich. Bidh an fheadhainn ùr-ghnàthach seo a’ brosnachadh oileanaich a dhol an sàs gu for-ghnìomhach agus eadar-obrachadh leis na co-oileanaich aca agus thusa - an tidsear - rè leasanan. Feumaidh oileanaich barrachd obrach a dhèanamh, ach ann an dòigh a choinnicheas ri na feumalachdan aca nas fheàrr agus a chuidicheas iad gus fàs nas luaithe.
Eu-coltach ri teagasg traidiseanta, a tha gu sònraichte ag amas air an ìre de eòlas as urrainn dhut a thoirt do na h-oileanaich agad, bidh dòighean teagaisg ùr-ghnàthach a’ cladhach gu domhainn a-steach do na tha oileanaich dha-rìribh a’ toirt air falbh bho na tha thu a’ teagasg aig òraidean.
Carson a dh'fheumas tidsearan a bhith ùr-ghnàthach
Tha an gluasad gu ionnsachadh air-loidhne agus measgaichte air fìrinn chruaidh fhoillseachadh: tha e gu math furasta do dh’ oileanaich a bhith air an sgaradh air cùl an sgrion. Tha mòran air ealain a bhith a’ coimhead an sàs fhad ‘s a tha an inntinnean a’ siubhal ann an àiteachan eile (no nas miosa, fhad ‘s a tha iad san leabaidh!) a leasachadh.
Ach seo an rud – chan urrainn dhuinn a’ choire gu lèir a chur air oileanaich. Mar luchd-foghlaim, tha dleastanas oirnn leasanan a chruthachadh a ghlacas aire agus a chumas an luchd-ionnsachaidh an sàs. Chan eil teagasg tioram, aon-fhillte gu leòr tuilleadh, ge bith dè an dòigh lìbhrigidh a thathar a’ cleachdadh.
Tha na h-àireamhan ag innse sgeulachd inntinneach. Dàta o chionn ghoirid bho gabhail ri teicneòlas foghlaim taisbeanaidhean:
- Tha innealan ionnsachaidh didseatach aig 57% de dh’ oileanaich sna SA a-nis
- Chuir 75% de sgoiltean sna SA comasan brìgheil slàn an gnìomh no bha iad an dùil an cleachdadh
- Tha àrd-ùrlaran foghlaim cunntachail airson 40% de chleachdadh innealan oileanach
- Chunnaic aplacaidean riaghlaidh ionnsachaidh iomallach àrdachadh 87% ann an gabhail riutha
- Leum cleachdadh aplacaidean co-obrachaidh 141%
- Tha 80% de ionadan foghlaim air tasgadh a dhèanamh ann an innealan teicneòlais ùra
- Thug 98% de dh'oilthighean seachad teagasg air-loidhne
Tha na staitistig seo a’ nochdadh atharrachadh bunaiteach ann an mar a bhios sinn a’ teagasg agus ag ionnsachadh. Na bi air do fhàgail às do dhèidh le dòighean seann-fhasanta—tha an t-àm ann ath-smaoineachadh air do dhòigh-obrach a thaobh foghlaim.
15 Dòighean Teagaisg Ùr-ghnàthach
1. Leasanan eadar-ghnìomhach
Is e oileanaich an luchd-ionnsachaidh ùr-ghnàthach agad! Tha leasanan aon-shligheach gu math traidiseanta agus uaireannan sgìth dhut fhèin agus do na h-oileanaich agad, mar sin cruthaich àrainneachd far am bi oileanaich a’ faireachdainn gu bheil iad air am brosnachadh gus bruidhinn agus am beachdan a chuir an cèill.
Faodaidh oileanaich a dhol an sàs ann an gnìomhan sa chlas ann an iomadh dòigh, chan ann dìreach le bhith a’ togail an làmhan no a bhith air an gairm airson freagairt. An-diugh, gheibh thu àrd-ùrlaran air-loidhne a chuidicheas tu gus gnìomhan clasa eadar-ghnìomhach a dhèanamh gus tòrr ùine a shàbhaladh agus toirt air a h-uile oileanach a thighinn còmhla an àite dìreach dhà no trì.
🌟 Eisimpleirean leasain eadar-ghnìomhach
Tha àrd-ùrlaran eadar-ghnìomhach an latha an-diugh air ath-bhualadh a thoirt air com-pàirteachadh sa chlas. An àite a bhith an urra ris na h-aon trì oileanaich a bhios an-còmhnaidh a’ togail an làmhan, faodaidh tu do chlas gu lèir a thoirt a-steach troimhe. ceisteachain beò, cunntasan-bheachd, sgòthan facal, seiseanan C&F, agus gnìomhan co-obrachail airson beachdan a chruinneachadh.
Chan e a-mhàin sin, ach faodaidh oileanaich freagairtean a thaipeadh no a thaghadh gun urra an àite a bhith a’ togail an làmhan. Tha seo gam fàgail nas misneachaile a dhol an sàs, am beachdan a chur an cèill agus gun a bhith a’ gabhail dragh tuilleadh mu bhith ‘ceàrr’ no air am breithneachadh.
Tip practaigeach: Tòisich an ath leasan agad le cunntas-bheachd gun urra a’ faighneachd do dh’ oileanaich dè tha fios aca mu thràth mun chuspair. Cleachd na toraidhean gus an teagasg agad atharrachadh air an t-slighe, a’ dèiligeadh ri mì-thuigse agus a’ togail air eòlas a th’ ann mar-thà.
2. A 'cleachdadh teicneòlas virtual reality
Smaoinich air na sgoilearan agad a’ sgrùdadh uachdar Mhars, a’ coiseachd tro sheann Ròimh, no a’ crìonadh sìos gus ceallan fhaicinn bhon taobh a-staigh. Sin cumhachd VR ann am foghlam—bidh e ag atharrachadh bun-bheachdan eas-chruthach gu eòlasan làimhseachail, cuimhneachail.
Bidh teicneòlas VR a’ cruthachadh àrainneachdan ionnsachaidh inntinneach far am bi oileanaich ag eadar-obrachadh le riochdachaidhean trì-thaobhach seach ìomhaighean statach ann an leabhraichean teacsa. Faodaidh iad nithean a làimhseachadh, àiteachan a rannsachadh, agus suidheachaidhean a lorg a bhiodh do-dhèanta no neo-phractaigeach ann am fìor bheatha.
'S e, tha uidheamachd VR a' riochdachadh tasgadh mòr. Ach gu tric bidh a' bhuaidh air com-pàirteachadh agus gleidheadh oileanach a' fìreanachadh a' chosgais. Bidh oileanaich a' cuimhneachadh eòlasan fada nas fheàrr na òraidean, agus bidh VR a' cruthachadh amannan ionnsachaidh nach dìochuimhnich thu gu bràth.
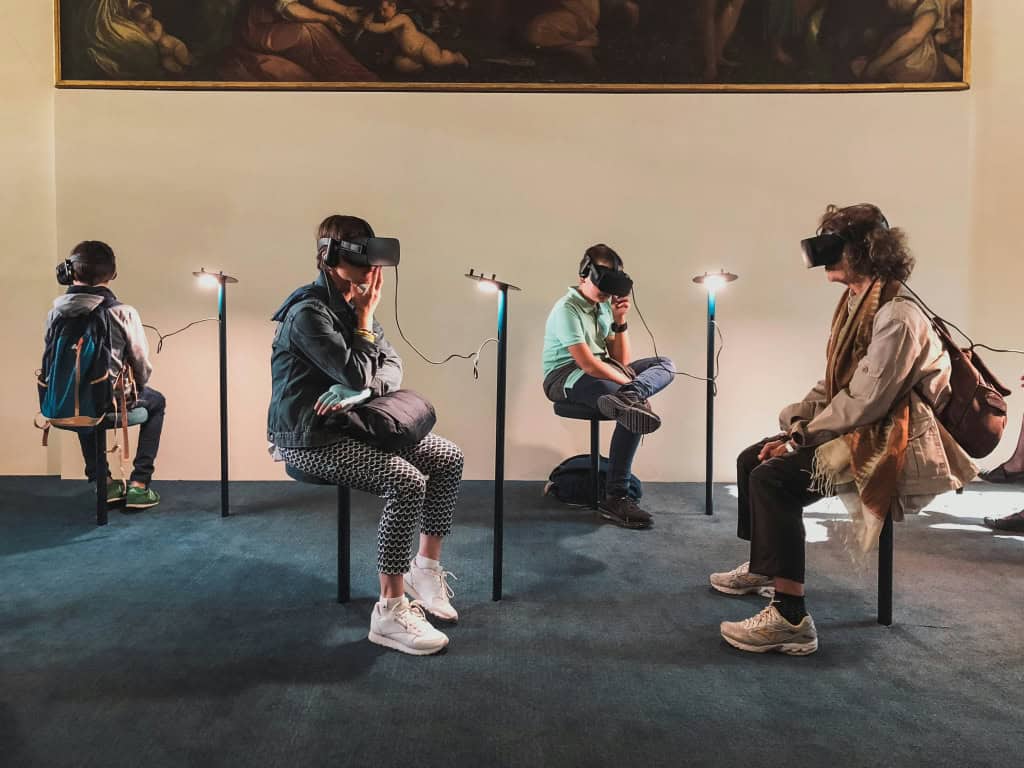

🌟 Teagasg le Teicneòlas Virtual Reality
Tha e a’ coimhead spòrsail, ach ciamar a bhios tidsearan a’ teagasg le teicneòlas VR airson fìor? Coimhead air a’ bhidio seo de sheisean VR le Acadamaidh Tablet.
3. A 'cleachdadh AI ann am foghlam
Bruidhinnidh sinn ris an ailbhean anns an t-seòmar: chan eil AI an seo gus àite thidsearan a ghabhail. An àite sin, 's e inneal cumhachdach a th' ann gus an obair agad a lughdachadh agus teagasg a phearsanachadh ann an dòighean nach robh comasach roimhe.
Tha e coltach gu bheil thu mu thràth a’ cleachdadh innealan le cumhachd AI gun fhios dhut – bidh siostaman riaghlaidh ionnsachaidh, luchd-sgrùdaidh meirle-sgrìobhaidh, ìrean fèin-ghluasadach, agus àrd-ùrlaran ionnsachaidh atharrachail uile a’ cleachdadh inntleachd shaorga. Bidh na h-innealan sin a’ dèiligeadh ri gnìomhan rianachd a bheir ùine mhòr, gad shaoradh gus fòcas a chuir air na rudan a tha dha-rìribh cudromach: ceangal ri oileanaich agus ionnsachadh domhainn a dhèanamh comasach.
Tha AI air leth math ann an grunn thagraidhean foghlaim:
- Stiùireadh cùrsa - A’ cur stuthan air dòigh, a’ cumail sùil air adhartas, agus a’ riaghladh obair-dachaigh
- Ionnsachadh freagarrach – Ag atharrachadh duilgheadas agus susbaint a rèir coileanadh nan oileanach fa leth
- conaltradh – A’ dèanamh ceanglaichean eadar pàrantan is tidsearan nas fhasa agus a’ toirt taic do dh’oileanaich
- Cruthachadh susbaint – A’ cruthachadh stuthan ionnsachaidh agus measadh gnàthaichte
Facal rabhaidh: Cleachd AI mar neach-cuideachaidh teagaisg, chan ann an àite breithneachadh daonna. Dèan ath-sgrùdadh an-còmhnaidh air susbaint a chaidh a chruthachadh le AI agus cùm ceangal pearsanta ri oileanaich, chan e sin rudeigin nach urrainn do algairim sam bith ath-riochdachadh.
4. Ionnsachadh coimeasgaichte
Bidh ionnsachadh measgaichte a’ cothlamadh an rud as fheàrr den dà shaoghal: teagasg aghaidh-ri-aghaidh agus eòlasan ionnsachaidh didseatach. Tha an dòigh-obrach seo a’ tabhann sùbailteachd do thidsearan agus do dh’ oileanaich agus aig an aon àm a’ cumail suas a’ cheangail phearsanta a tha a’ dèanamh foghlam brìoghmhor.
Anns an t-saoghal againn a tha làn teicneòlais, bhiodh e gòrach innealan didseatach cumhachdach a leigeil seachad. Tha co-labhairtean bhidio, siostaman riaghlaidh ionnsachaidh, àrd-ùrlaran eadar-ghnìomhach, agus gun àireamh de aplacaidean foghlaim air an luach a dhearbhadh. Ach tha teagasg aghaidh-ri-aghaidh air a bhith mar an ceudna, leis na còmhraidhean gun spionnadh, am fios-air-ais sa bhad, agus an ceangal daonna.
Leigidh ionnsachadh measgaichte leat teicneòlas a chleachdadh gus teagasg traidiseanta a leasachadh – chan e a chur na àite. Dh’fhaodadh oileanaich bhideothan teagaisg fhaicinn aig an taigh, agus an uairsin ùine sa chlas a chleachdadh airson gnìomhan practaigeach, deasbadan, agus pròiseactan co-obrachail. No dh’fhaodadh tu innealan didseatach a chleachdadh rè leasanan pearsanta gus conaltradh a mheudachadh agus fios-air-ais fìor-ùine a chruinneachadh.
Beachd cur an gnìomh: Cruthaich aonad “air a thionndadh” far am bi oileanaich a’ coimhead leasanan bhidio goirid aig an taigh (no rè ùine obrach neo-eisimeileach), agus an uairsin a’ cleachdadh seiseanan clas airson gnìomhan tagraidh, fuasgladh cheistean, agus co-obrachadh le co-aoisean. Bidh seo a’ meudachadh ùine luachmhor aghaidh-ri-aghaidh.
5. Clò-bhualadh 3D
Bheir clò-bhualadh 3D bun-bheachdan eas-chruthach do làmhan nan oileanach—gu litireil. Tha rudeigin cumhachdach ann a bhith a’ cumail agus a’ sgrùdadh modail nach urrainn dha ìomhaighean rèidh agus diagraman a mhaidseadh idir.
Faodaidh oileanaich modalan anatomaigeach a làimhseachadh gus tuigse fhaighinn air siostaman a’ chuirp, sgrùdadh a dhèanamh air structaran ailtireil bho gach ceàrn, seann stuthan a chruthachadh, prototypes innleadaireachd a dhealbhadh, no bun-bheachdan matamataigeach a shamhlachadh. Tha na cothroman a’ dol thairis air gach raon cuspair.
A bharrachd air dìreach a bhith a’ coimhead air nithean clò-bhuailte 3D, bidh am pròiseas dealbhaidh fhèin a’ teagasg sgilean luachmhor. Nuair a chruthaicheas oileanaich na modailean aca fhèin, bidh iad a’ leasachadh reusanachadh fànais, comasan fuasgladh-cheistean, agus smaoineachadh dealbhaidh ath-aithriseach.
Dòigh-obrach càirdeil don bhuidseit: Mura h-eil clò-bhualadair 3D aig an sgoil agad, tha mòran leabharlannan ionadail, àiteachan-dèanaidh, agus goireasan oilthigh a’ tabhann ruigsinneachd don phoball. Faodaidh seirbheisean air-loidhne dealbhaidhean a chlò-bhualadh agus a chuir air falbh gu saor cuideachd. Tòisich le bhith a’ luchdachadh sìos modalan foghlaim an-asgaidh mus tasgadh thu anns an uidheamachd agad fhèin.
6. Cleachd am pròiseas dealbhaidh-smaoineachaidh
Tha am fear seo na ro-innleachd stèidhichte air fuasgladh gus fuasgladh fhaighinn air duilgheadasan, co-obrachadh agus spionnadh cruthachail oileanaich. Tha còig ìrean ann, ach tha e eadar-dhealaichte bho dhòighean eile oir chan fheum thu stiùireadh ceum air cheum no òrdugh sam bith a leantainn. Is e pròiseas neo-loidhneach a th’ ann, agus mar sin faodaidh tu a ghnàthachadh a rèir na h-òraidean agus na gnìomhan agad.
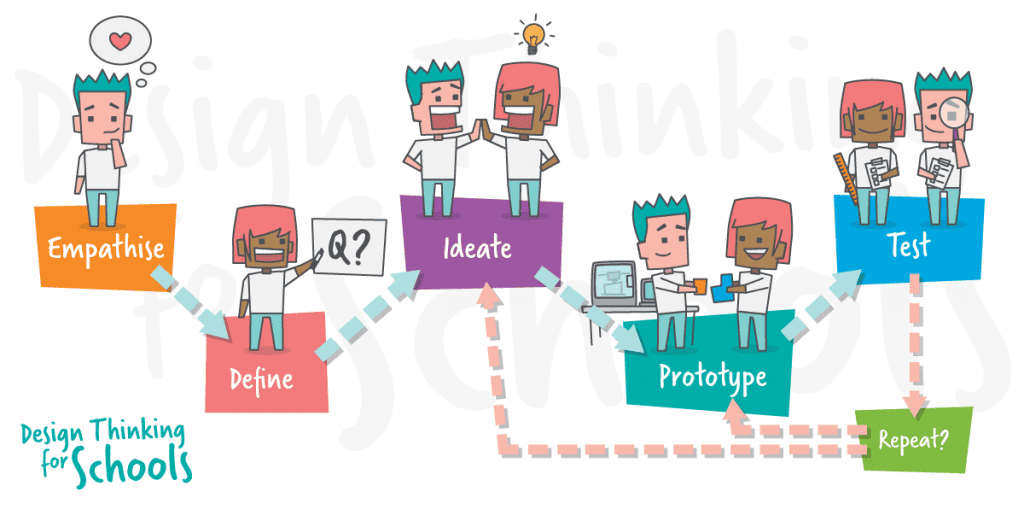
Is iad na còig ìrean:
- Dèan co-fhaireachdainn - Leasaich co-fhaireachdainn, agus faigh a-mach na feumalachdan airson na fuasglaidhean.
- Sgrìobh - Mìnich cùisean agus na cothroman air dèiligeadh riutha.
- Smaoinich - Smaoinich agus cruthaich beachdan ùra, cruthachail.
- Prototype - Dèan dreach no sampall de na fuasglaidhean gus na beachdan a sgrùdadh tuilleadh.
- deuchainn - Dèan deuchainn air na fuasglaidhean, dèan measadh agus cruinnich fios air ais.
🌟 Eisimpleir de phròiseas dealbhaidh-smaoineachaidh
A bheil thu airson faicinn mar a thèid e ann an clas fìor? Seo mar a bhios oileanaich K-8 aig Design 39 Campus ag obair leis an fhrèam seo.
7. Ionnsachadh stèidhichte air pròiseact
Bidh ionnsachadh stèidhichte air pròiseactan (PBL) a’ tionndadh foghlam traidiseanta bun os cionn. An àite a bhith ag ionnsachadh susbaint an toiseach agus ga chur an sàs nas fhaide air adhart, bidh oileanaich a’ dèiligeadh ri duilgheadasan san t-saoghal fhìor a dh’ fheumas iad susbaint agus sgilean ùra ionnsachadh air an t-slighe.
Am prìomh eadar-dhealachadh bho phròiseactan àbhaisteach aig deireadh aonaid: ’S e eòlas ionnsachaidh a th’ ann am pròiseactan PBL, chan e dìreach measadh a thèid a chur ris aig a’ cheann thall. Bidh oileanaich ag obair thar ùine mhòr, a’ leasachadh sgilean rannsachaidh, smaoineachadh breithneachail, comasan co-obrachaidh, agus eòlas air a’ chuspair aig an aon àm.
Bidh an dreuchd agad ag atharrachadh bho bhith a’ lìbhrigeadh fiosrachaidh gu bhith na chomhairliche agus na stiùiriche. Bidh oileanaich a’ gabhail uallach airson an turas ionnsachaidh, a tha a’ meudachadh gu mòr an com-pàirteachaidh agus an gleidheadh. Chan e a-mhàin gu bheil iad a’ cuimhneachadh fhìrinnean—tha iad a’ cur an sàs eòlais gus rudeigin brìoghmhor a chruthachadh.
prògraman beachdan pròiseict gabhail a-steach:
- A’ filmeadh prògram aithriseach mu chùis shòisealta ionadail
- A’ dealbhadh agus a’ cur air dòigh tachartas sgoile no tachartas togail-airgid
- A’ riaghladh iomairt nam meadhanan sòisealta airson buidheann coimhearsnachd
- A’ cruthachadh mion-sgrùdaidhean lèirsinneach air duilgheadasan sòisealta le fuasglaidhean a thathar a’ moladh
- A’ leasachadh phlanaichean seasmhachd airson ghnìomhachasan ionadail
Molaidhean airson soirbheachas: Dèan cinnteach gu bheil luchd-èisteachd dearbhte aig pròiseactan a bharrachd air thusa a-mhàin. Nuair a bhios oileanaich a’ taisbeanadh do bhuill a’ choimhearsnachd, proifeiseantaich ionadail, no oileanaich nas òige, tha na geallaidhean a’ faireachdainn fìor agus bidh am brosnachadh ag èirigh gu mòr.
8. Ionnsachadh stèidhichte air rannsachadh
Bidh ionnsachadh stèidhichte air rannsachadh a’ tòiseachadh le ceistean, chan e freagairtean. An àite òraid a thoirt seachad agus an uairsin tuigse a mheasadh, bidh thu a’ cur dhuilgheadasan no suidheachaidhean air am feum oileanaich sgrùdadh a dhèanamh leotha fhèin no ann an co-obrachadh.
Bidh an dòigh seo gad shuidheachadh mar neach-comasachaidh seach mar òraidiche. Bidh oileanaich a’ leasachadh sgilean rannsachaidh, smaoineachadh breithneachail, agus comasan ionnsachaidh fèin-stiùirichte fhad ‘s a bhios iad a’ sireadh fhreagairtean do cheistean inntinneach.
Mar as trice bidh am pròiseas a’ toirt a-steach oileanaich:
- A’ coinneachadh ri duilgheadas no ceist
- A’ cruthachadh barailean no ro-innsean
- Dealbhadh rannsachaidhean no dhòighean-obrach rannsachaidh
- A’ cruinneachadh agus a’ sgrùdadh fiosrachaidh
- A’ tarraing cho-dhùnaidhean agus a’ meòrachadh air na co-dhùnaidhean
- A’ conaltradh thoraidhean ri feadhainn eile
Dh’fhaodadh suidheachaidhean stèidhichte air rannsachadh a bhith a’ gabhail a-steach:
- A’ sgrùdadh thùsan truailleadh sa choimhearsnachd agad agus a’ moladh fhuasglaidhean
- A’ dèanamh deuchainnean air fàs lusan fo dhiofar shuidheachaidhean
- A’ measadh èifeachdas phoileasaidhean sgoile a tha ann mar-thà
- Ceistean rannsachaidh a bhios oileanaich a’ cruthachadh iad fhèin mu chuspairean inntinneach
Molaidhean airson sgafaill: Tòisich le rannsachadh structarail far am bi thu a’ toirt seachad a’ cheist agus an dòigh-obrach, agus an uairsin mean air mhean leig às an uallach gus am bi oileanaich a’ gineadh na ceistean aca fhèin agus a’ dealbhadh rannsachaidhean leotha fhèin.
9. Measg
Coltach ri tòimhseachan a chur ri chèile, bidh an ro-innleachd ionnsachaidh cho-obrachail seo ag iarraidh air oileanaich an eòlas coitcheann aca a chur ri chèile gus dealbh iomlan den chuspair a chruthachadh.
Seo mar a tha e ag obair:
- Roinn do chlas ann am buidhnean beaga
- Sònraich fo-chuspair no taobh eadar-dhealaichte den phrìomh chuspair do gach buidheann
- Thoir air buidhnean rannsachadh a dhèanamh agus a bhith nan “eòlaichean” air a’ phìos a chaidh a shònrachadh dhaibh
- Bidh gach buidheann a’ taisbeanadh na toraidhean aca don chlas
- Còmhla, bidh na taisbeanaidhean a’ cruthachadh tuigse iomlan air a’ chuspair gu lèir.
- Roghainneil, seiseanan fios-air-ais co-aoisean a chur air dòigh far am bi buidhnean a’ measadh obair a chèile
Airson clasaichean le barrachd eòlais, faodaidh tu fo-chuspairean eadar-dhealaichte a thoirt do dh’ oileanaich fa leth. Bidh iad an toiseach a’ coinneachadh ri co-oileanaich a tha ag ionnsachadh an aon fho-chuspair (buidhnean eòlaichean), agus an uairsin a’ tilleadh chun na buidhnean tùsail aca gus na dh’ ionnsaich iad a theagasg.
Eisimpleirean sònraichte don chuspair:
- Ealain cànain: Sònraich diofar eileamaidean litreachail (caractaran, suidheachadh, cuspairean, samhlachas) bhon aon nobhail do bhuidhnean
- eachdraidh: Iarr air buidhnean rannsachadh a dhèanamh air diofar thaobhan de thachartas eachdraidheil (adhbharan, prìomh dhaoine, prìomh bhlàran, builean, dìleab)
- Saidheans: Bidh oileanaich a’ sgrùdadh diofar shiostaman bodhaig, agus an uairsin a’ teagasg do cho-oileanaich mar a tha iad ag eadar-cheangal
Carson a tha e ag obair: Feumaidh tuigse nas doimhne na dìreach a bhith ga sgrùdadh a bhith agad airson susbaint a theagasg do cho-aoisean. Feumaidh oileanaich am pìos aca a thuigsinn gu ceart gus a mhìneachadh gu soilleir, agus tha iad cunntachail dha na co-oileanaich aca, chan ann dìreach dhutsa.
10. Ionnsachadh air a stiùireadh le rannsachadh
Bidh ionnsachadh air a stiùireadh le rannsachadh a’ cur fiosrachd aig cridhe foghlaim. An àite tidsearan a bhith a’ lìbhrigeadh a h-uile freagairt, bidh oileanaich a’ stiùireadh an ionnsachaidh fhèin le bhith a’ faighneachd cheistean, a’ sgrùdadh chuspairean, agus a’ togail eòlais tro rannsachadh agus lorg.
Bidh an dòigh-obrach seo ag atharrachadh oileanaich bho bhith nan luchd-gabhail fulangach gu bhith nan luchd-sgrùdaidh gnìomhach. Bidh tidsearan ag obair mar luchd-comasachaidh a bhios a’ stiùireadh a’ phròiseis rannsachaidh seach a bhith nan luchd-geata fiosrachaidh. Bidh oileanaich a’ leasachadh smaoineachadh breithneachail, sgilean rannsachaidh, agus tuigse nas doimhne leis gu bheil iad gu pearsanta an sàs ann a bhith a’ lorg fhreagairtean do cheistean a tha cudromach dhaibh.
Mar as trice bidh cearcall an rannsachaidh a’ dol tro ìrean: bidh oileanaich a’ cur cheistean, a’ dealbhadh rannsachaidhean, a’ cruinneachadh agus a’ sgrùdadh fiosrachaidh, a’ tarraing cho-dhùnaidhean, agus a’ meòrachadh air na dh’ionnsaich iad. Tha seo a’ nochdadh mar a bhios fìor luchd-saidheans, eachdraichean agus proifeiseantaich ag obair san raon.
Is e an rud a tha a’ dèanamh ionnsachadh air a stiùireadh le rannsachadh gu sònraichte cumhachdach gu bheil e a’ teagasg do dh’ oileanaich ciamar airson ionnsachadh, chan ann a-mhàin dè airson ionnsachadh. Bidh iad a’ leasachadh comasan fuasgladh-cheistean agus seasmhachd nuair a bhios iad an aghaidh dhùbhlain, gan ullachadh airson ionnsachadh fad-beatha.
🌟 Eisimpleirean ionnsachaidh air an stiùireadh le rannsachadh
- Rannsachadh saidheansAn àite innse do dh’oileanaich mar a bhios lusan a’ fàs, faighnich “Dè a dh’fheumas lusan airson a bhith beò?” Leig le oileanaich deuchainnean a dhealbhadh a’ dèanamh deuchainn air diofar chaochladairean leithid solas, uisge agus càileachd na h-ùire.
- Rannsachadh eachdraidheilAn àite a bhith a’ toirt òraid mu thachartas eachdraidheil, cuir ceist mar “Carson a thuit Balla Bherlin?” Bidh oileanaich a’ rannsachadh iomadh sealladh, prìomh thùsan, agus co-theacsan eachdraidheil gus an tuigse a thogail.
- Rannsachadh matamataigTaisbean duilgheadas san t-saoghal fhìor: “Ciamar as urrainn dhuinn raon-cluiche na sgoile againn ath-dhealbhadh gus na raointean-cluiche as fheàrr fhaighinn taobh a-staigh a’ bhuidseit?” Bidh oileanaich a’ cleachdadh bun-bheachdan matamataigeach fhad ’s a tha iad a’ sgrùdadh fhuasglaidhean practaigeach.
11. Flipped clas
Tha modail seòmar-sgoile air a thionndadh a’ cur an teagasg traidiseanta bun os cionn: tha lìbhrigeadh susbaint a’ tachairt aig an taigh, agus cleachdadh is cur an sàs a’ tachairt sa chlas.
Ron chlas, bidh oileanaich a’ coimhead bhideothan, a’ leughadh stuthan, no a’ sgrùdadh ghoireasan gus eòlas bunaiteach fhaighinn. An uairsin, bidh ùine luachmhor sa chlas air a choisrigeadh do ghnìomhachdan a thathas a’ meas gu traidiseanta mar “obair-dachaigh” - a’ cur bun-bheachdan an sàs, a’ fuasgladh dhuilgheadasan, a’ beachdachadh air beachdan, agus ag obair còmhla air pròiseactan.
Tha grunn bhuannachdan aig an dòigh-obrach seo. Faodaidh oileanaich stad a chuir air susbaint teagaisg, ath-fhilleadh air, agus ath-choimhead mar a dh’ fheumar, ag ionnsachadh aig an astar fhèin. Gheibh oileanaich a tha a’ strì ùine a bharrachd le stuth bunaiteach, agus faodaidh oileanaich adhartach gluasad gu sgiobalta tro na bunaitean agus sgrùdadh nas doimhne a dhèanamh air leudachadh.
Aig an aon àm, bidh thu ri fhaotainn tron chlas airson na h-amannan nuair a bhios feum as motha aig oileanaich ort - nuair a bhios iad a’ dèiligeadh ri tagraidhean dùbhlanach, gun a bhith ag èisteachd gu fulangach ri mìneachaidhean.
Ro-innleachd cur an gnìomh: Cruthaich leasanan bhidio goirid, fòcasach (5-10 mionaidean aig a’ char as àirde). Bidh ùine aire goirid aig oileanaich le susbaint clàraichte, mar sin cùm e goirid agus inntinneach. Cleachd ùine sa chlas airson gnìomhan practaigeach, deasbadan, agus fuasgladh-cheistean co-obrachail far a bheil do eòlas a’ cur fìor luach ris.
Ag iarraidh faighinn a-mach mar a tha seòmar-sgoile air a thionndadh a’ coimhead agus a’ tachairt ann am fìor bheathaThoir sùil air a’ bhidio seo le McGraw-Hill mun chlas aca a chaidh a thionndadh.
12. Teagasg Chomhaoisean
Tha am fear seo coltach ris na tha sinn air a dheasbad anns an dòigh jigsaw. Bidh oileanaich a’ tuigsinn agus a’ maighstireachd eòlas nas fheàrr nuair as urrainn dhaibh a mhìneachadh gu soilleir. Nuair a bhios iad a’ taisbeanadh, is dòcha gun ionnsaich iad le cridhe ro-làimh agus na tha iad a’ cuimhneachadh a bhruidhinn a-mach, ach gus an co-aoisean a theagasg, feumaidh iad an duilgheadas a thuigsinn gu mionaideach.
Faodaidh oileanaich a bhith air thoiseach sa ghnìomhachd seo le bhith a’ taghadh an raon ùidhe aca taobh a-staigh a’ chuspair. Le bhith a’ toirt an seòrsa fèin-riaghlaidh seo do dh’ oileanaich bidh iad gan cuideachadh gus faireachdainn gu bheil seilbh aca air a’ chuspair agus an dleastanas a bhith ga theagasg ceart.
Lorgaidh tu cuideachd gu bheil a bhith a’ toirt cothrom do dh’ oileanaich an luchd-clas a theagasg a’ togail am misneachd, a’ brosnachadh ionnsachadh neo-eisimeileach, agus a’ leasachadh sgilean taisbeanaidh.
🌟 Eisimpleirean Teagasg Cho-aoisean
Coimhead air a’ bhidio seo de leasan matamataigeach nàdarrach fiùghantach air a theagasg le oileanach òg aig Àrd-sgoil Ealain Lèirsinneach is Dealbhaidh Dulwich!
13. Teagasg atharrachail le anailitigeachd ionnsachaidh
Bidh teagasg atharrachail a’ cleachdadh dàta agus teicneòlas gus stiùireadh a phearsanachadh do gach oileanach ann an àm fìor. Bidh innealan anailis ionnsachaidh a’ tional fiosrachadh mu choileanadh, com-pàirteachadh agus pàtrain ionnsachaidh nan oileanach, agus an uairsin a’ cuideachadh thidsearan gus na ro-innleachdan teagaisg aca atharrachadh gus coinneachadh ri feumalachdan fa leth.
Tha an dòigh seo a’ dol nas fhaide na teagasg traidiseanta aon-mheudach a fhreagras air a h-uile duine le bhith ag aithneachadh gu bheil gach oileanach ag ionnsachadh ann an dòigh eadar-dhealaichte agus aig an astar fhèin. Faodaidh tidsearan clàran-stiùiridh agus aithisgean a chleachdadh gus faighinn a-mach dè na h-oileanaich a dh’ fheumas taic a bharrachd, dè na h-oileanaich a tha deiseil airson stuth nas dùbhlanaiche, agus dè na bun-bheachdan leis a bheil a’ chlas gu lèir a’ strì.
Bidh àrd-ùrlaran anailis ionnsachaidh a’ cumail sùil air a h-uile càil bho sgòran cheisteachain agus crìochnachadh obair-dachaigh gu ùine a thathar a’ cosg air gnìomhan agus pàtrain eadar-obrachaidh. Bidh an dàta seo a’ toirt lèirsinn obrachail do thidsearan gun a bhith an urra ri faireachdainnean gut no deuchainnean cunbhalach a-mhàin.
🌟 Teagasg atharrachail le eisimpleirean de anailiseachd ionnsachaidh
Dàta siostam riaghlaidh ionnsachaidh (LMS)Àrd-ùrlaran mar Google Classroom, Canvas, no bidh Moodle a’ cumail sùil air meatairean conaltraidh nan oileanach—cuin a bhios oileanaich a’ faighinn cothrom air stuthan, dè cho fada ’s a bhios iad a’ leughadh, dè na goireasan air an tèid iad a-rithist. Faodaidh tidsearan fios a chuir gu oileanaich a tha a’ sealltainn phàtranan dì-cheangal mus tuit iad air dheireadh.
Àrd-ùrlaran ionnsachaidh freagarrachCleachd innealan mar Khan Academy no IXL a bhios ag atharrachadh duilgheadas cheistean gu fèin-ghluasadach stèidhichte air freagairtean nan oileanach. Gheibh tidsearan aithisgean mionaideach a’ sealltainn dè na bun-bheachdan a tha gach oileanach air a mhaighstir agus càite a bheil iad a’ strì.
Measadh cruthachail ann an àm fìorRè na leasanan, cleachd àrd-ùrlaran mar AhaSlides no Kahoot gus sgrùdaidhean luath a dhèanamh airson tuigseBidh anailitigeachd a’ sealltainn sa bhad dè na h-oileanaich a fhuair ceistean ceart no ceàrr, a’ leigeil leat bun-bheachdan ath-theagasg sa bhad no buidhnean beaga cuimsichte a chruthachadh.
14. Teagasg crossover
A bheil cuimhne agad cho togarrach a bha thu nuair a chaidh do chlas gu taigh-tasgaidh, taisbeanadh no turas-raoin? Tha e an-còmhnaidh na spreadhadh a dhol a-mach agus rudeigin eadar-dhealaichte a dhèanamh bho bhith a’ coimhead air a’ bhòrd ann an seòmar-sgoile.
Tha teagasg crossover a’ ceangal eòlas ionnsachaidh an dà chuid sa chlas agus àite a-muigh. Rannsaich bun-bheachdan san sgoil còmhla, agus an uairsin cuir turas air dòigh gu àite sònraichte far an urrainn dhut sealltainn mar a tha am bun-bheachd sin ag obair ann an suidheachadh fìor.
Bhiodh e eadhon na b’ èifeachdaiche an leasan a leasachadh le bhith a’ cumail chòmhraidhean no a’ sònrachadh obair buidhne sa chlas às deidh an turais.
🌟 Eisimpleir teagaisg crossover mas-fhìor
Aig amannan, chan eil e an-còmhnaidh comasach a dhol a-mach, ach tha dòighean ann timcheall air sin. Thoir sùil air an turas brìgheil Museum of Modern Art còmhla ri Mrs Gauthier bho Southfield School Art.
15. Ionnsachadh pearsanaichte
Seo fìrinn mì-chofhurtail: tha na tha ag obair gu sgoinneil do chuid de dh’ oileanaich a’ fàiligeadh gu tur do chàch. Bidh gnìomhachdan buidhne a’ toirt spionnadh do dh’ oileanaich a tha a-muigh ach a’ cur cus cuideam air daoine a tha a-staigh. Bidh luchd-ionnsachaidh lèirsinneach a’ soirbheachadh le diagraman ach is fheàrr le luchd-ionnsachaidh labhairteach deasbad. Bidh leasanan luath a’ tàladh cuid fhad ‘s a tha iad a’ fàgail feadhainn eile às an dèidh.
Tha ionnsachadh pearsanaichte ag aithneachadh nan eadar-dhealachaidhean seo agus a’ dèanamh an teagaisg freagarrach do ùidhean, feumalachdan, neartan agus laigsean nan oileanach fa leth. 'S e, feumaidh e barrachd ùine dealbhaidh ro-làimh. Ach tha am buannachd ann an coileanadh agus com-pàirteachadh nan oileanach mòr.
Chan eil pearsanachadh a’ ciallachadh leasanan gu tur eadar-dhealaichte a chruthachadh airson gach oileanach. An àite sin, tha e a’ ciallachadh roghainnean, astar sùbailte, dòighean measaidh eadar-dhealaichte, agus taic eadar-dhealaichte a thabhann.
Tha innealan didseatach a’ dèanamh pearsanachadh nas fhasa a riaghladh na bha e a-riamh. Bidh àrd-ùrlaran ionnsachaidh atharrachail ag atharrachadh duilgheadas gu fèin-ghluasadach, bidh siostaman riaghlaidh ionnsachaidh a’ cumail sùil air adhartas fa leth, agus leigidh diofar aplacaidean le oileanaich tuigse a nochdadh ann an iomadh dòigh.
Tòisich beag: Tòisich le bùird-roghainn far am bi oileanaich a’ taghadh bho ghrunn roghainnean airson obair-dachaigh no pròiseactan. No cleachd dàta measadh foirmeil gus buidhnean sùbailte a chruthachadh—uaireannan ag obair le oileanaich a tha a’ strì fhad ’s a bhios cuid eile a’ dèiligeadh ri leudachadh, amannan eile a’ cruinneachadh a rèir ùidh seach comas. Mean air mhean cuir a-steach barrachd pearsanachaidh mar a bhios tu a’ fàs comhfhurtail.
Ceistean Bitheanta
Ciamar a thaghas mi dè an dòigh ùr-ghnàthach a dh’fheuchas mi an toiseach?
Tòisich leis na tha a’ freagairt as fheàrr ri do stoidhle teagaisg agus na goireasan a tha rim faighinn. Ma tha thu comhfhurtail le teicneòlas, feuch leasanan eadar-ghnìomhach no seòmar-teagaisg air a thionndadh an toiseach. Ma tha thu ag iarraidh ionnsachadh practaigeach, feuch ionnsachadh stèidhichte air pròiseactan no an dòigh-obrach tòimhseachain. Na bi a’ faireachdainn fo chuideam a h-uile càil a ghabhail os làimh aig an aon àm - faodaidh eadhon aon dhòigh ùr buaidh mhòr a thoirt air com-pàirteachadh nan oileanach.
Dè ma thachras gum bi na h-oileanaich agam an aghaidh nan dòighean ùra seo?
Faodaidh atharrachadh a bhith mì-chofhurtail, gu h-àraidh do dh’ oileanaich a tha cleachdte ri ionnsachadh fulangach. Tòisich mean air mhean, mìnich carson a tha thu a’ feuchainn dhòighean-obrach ùra, agus bi foighidneach fhad ‘s a bhios oileanaich ag atharrachadh. Is fheàrr le mòran oileanaich dòighean traidiseanta an toiseach dìreach air sgàth ‘s gu bheil iad eòlach, chan ann air sgàth ‘s gu bheil iad nas èifeachdaiche. Cho luath ‘s a bhios oileanaich soirbheachail le dòighean-obrach ùr-ghnàthach, mar as trice bidh an strì a’ crìonadh.
Nach eil na dòighean seo a’ toirt cus ùine sa chlas?
An toiseach, tha—feumaidh cur an gnìomh dhòighean ùra ùine atharrachaidh. Ach cuimhnich, chan eil teagasg mu dheidhinn susbaint a chòmhdach; tha e mu dheidhinn oileanaich ag ionnsachadh susbaint. Bidh dòighean ùr-ghnàthach gu tric a’ leantainn gu tuigse nas doimhne, nas maireannaiche na òraidean traidiseanta, eadhon ged a bhios tu a’ còmhdach nas lugha de stuth. Tha càileachd nas cudromaiche na meud. A bharrachd air an sin, mar a bhios tu fhèin agus oileanaich eòlach air na dòighean-obrach sin, bidh iad a’ fàs nas èifeachdaiche.








