In the ever-changing world of organizations, figuring out and dealing with the main reasons for challenges is vital for long-term growth. Root Cause Analysis Method (RCA) is a structured approach that goes beyond addressing symptoms, aiming to reveal the real issues causing problems. By using RCA, organizations can improve their ability to solve problems, make processes more efficient, and cultivate a culture of ongoing improvement.
In this blog post, we'll explore what exactly the root cause analysis method is, its benefits, and 5 core RCA tools.
Table Of Contents
- What Is the Root Cause Analysis Method?
- Benefits Of Root Cause Analysis
- 5 Root Cause Analysis Tools
- Key Takeaways
- FAQs
What Is the Root Cause Analysis Method?

Root Cause Analysis Method is a structured and organized approach used to identify and resolve issues within an organization.
This method, also known as "root cause analysis," uses specific techniques to find the underlying causes of problems. It goes beyond surface-level symptoms to get to the root of the problem. By using this technique, organizations can identify core factors contributing to problems and develop effective solutions.
This approach is part of a broader methodology that emphasizes understanding and mitigating underlying causes to prevent the recurrence of problems and promote continuous improvement.
Benefits Of Root Cause Analysis
- Problem Prevention: Root Cause Analysis method helps in identifying the underlying causes of issues, allowing organizations to implement preventative measures. By addressing the root causes, organizations can proactively prevent the recurrence of problems, reducing the likelihood of future challenges.
- Improved Decision-Making: Root Cause Analysis method provides a deeper understanding of the factors contributing to problems, enabling informed decision-making. Organizations can make more strategic and effective decisions by considering the root causes, leading to better resource allocation and long-term solutions.
- Enhanced Problem-Solving Capabilities: RCA's systematic approach develops robust problem-solving skills in teams. It encourages thorough analysis, empowering efficient navigation of challenges and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
- Efficient Process Optimization: Finding root causes with Root Cause Analysis method allows streamlined operations. This leads to enhanced efficiency, reduced waste, and increased productivity as teams focus on addressing core issues in their workflow.
5 Root Cause Analysis Tools
To effectively implement the Root Cause Analysis Method, various tools are employed to systematically investigate and understand the factors contributing to problems. Here, we'll explore five essential tools widely used for Root Cause Analysis Method.
1/ Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa or Cause-and-Effect Diagram):
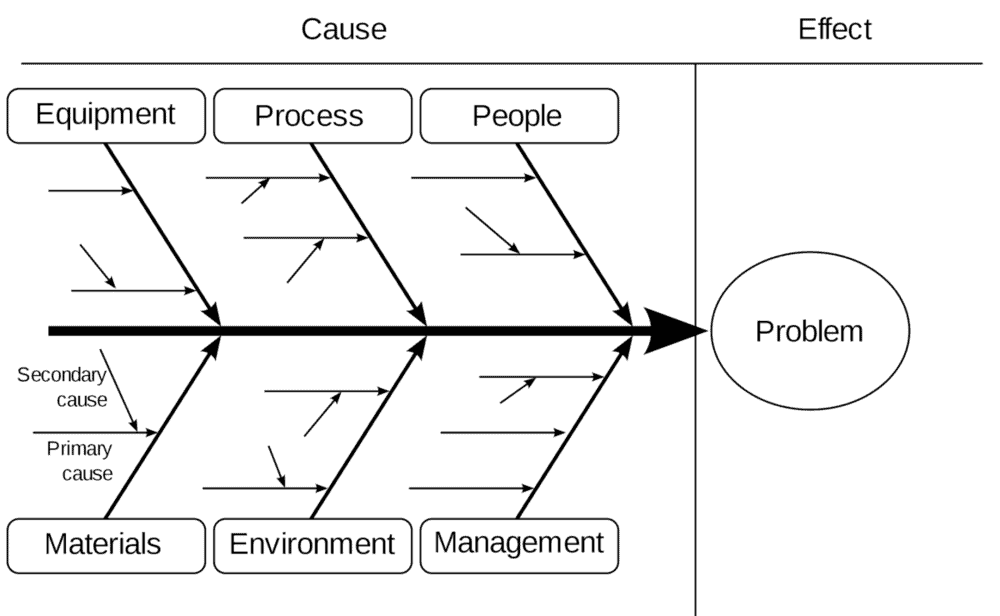
The fishbone diagram or root cause analysis fishbone method is a visual representation that aids in categorizing and exploring potential causes of a problem.
Its structure resembles a fish's skeleton, with the "bones" representing different categories such as people, processes, equipment, environment, and more. This tool encourages a holistic examination of various factors to identify the root cause, providing a comprehensive view of the problem landscape.
The process involves collaborative brainstorming sessions where team members contribute possible causes under each category. By visually organizing these inputs, the team gains insights into the interconnected relationships among different factors, facilitating a more targeted approach to root cause analysis.
2/ 5 Whys:
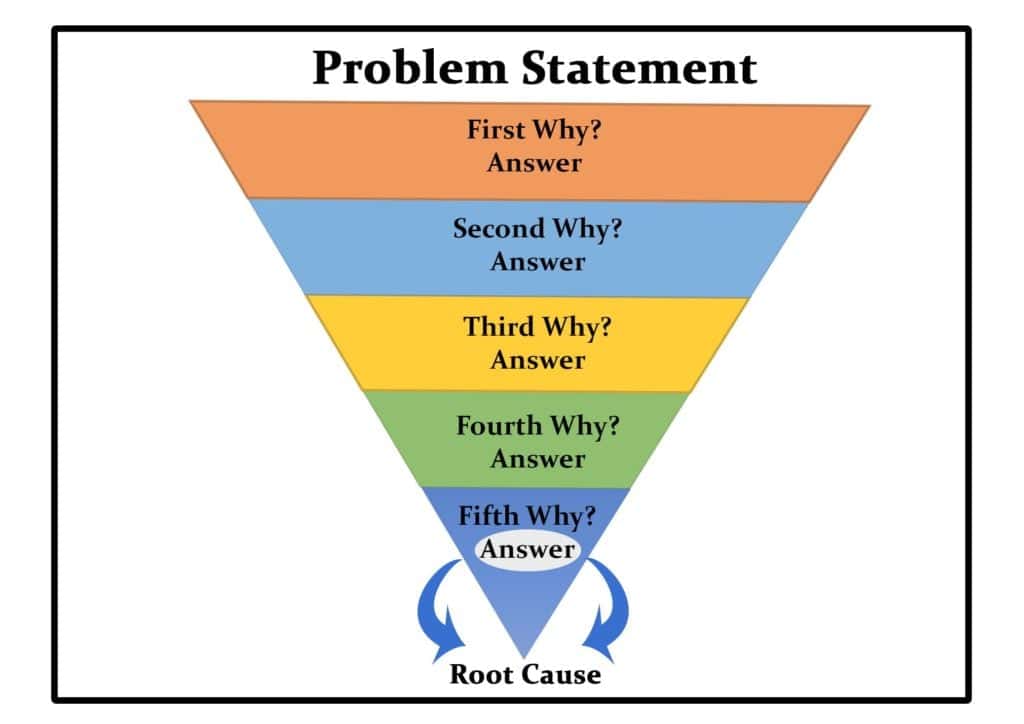
The 5 whys method of root cause analysis is a straightforward yet powerful questioning technique that encourages teams to repeatedly ask "why" until the fundamental cause of a problem is uncovered.
This tool delves deep into the layers of causation, promoting a thorough exploration of the issues at hand. The iterative nature of the questioning helps strip away surface-level symptoms, revealing the underlying factors contributing to the problem.
The 5 whys methodology of root cause analysis is effective for its simplicity and accessibility, making it a valuable tool for quick problem-solving and root cause identification. It encourages a continuous probing process that goes beyond initial responses to get to the heart of the matter.
3/ Pareto Analysis:
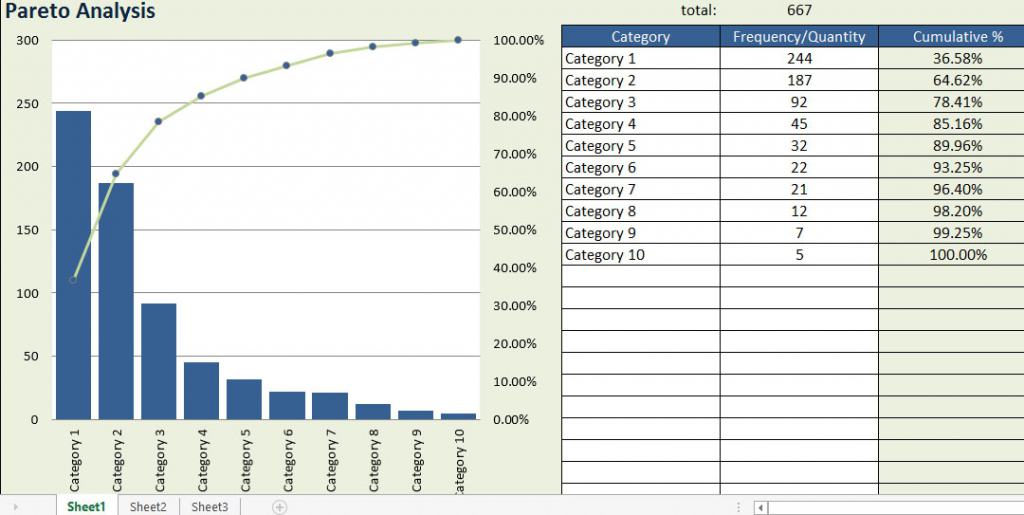
Pareto Analysis, based on the Pareto Principle, is a tool that helps prioritize issues by focusing on the significant few rather than the trivial many. The principle suggests that roughly 80% of effects come from 20% of causes. In the context of RCA, this means concentrating efforts on the vital few factors that contribute most significantly to the problem.
By applying Pareto Analysis, teams can identify and prioritize their efforts on addressing the critical root causes that will have the most substantial impact on problem resolution. This tool is particularly useful when resources are limited, ensuring a targeted and efficient approach to RCA.
4/ Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA):

Commonly utilized in manufacturing and engineering, Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) is a systematic approach to identify and prioritize potential failure modes in a process. FMEA evaluates the Severity, Occurrence, and Detection of potential failures, assigning scores to each criterion.
FMEA is a method that helps teams prioritize their focus on areas with the highest risk. By analyzing the potential impact, likelihood of occurrence, and ability to detect failures, teams can determine which areas require the most attention. This allows teams to efficiently allocate their resources and address potential issues before they become a problem.
5/ Scatter Diagram:
A Scatter Diagram is a visual tool employed in Root Cause Analysis to explore relationships between two variables.
By plotting data points on a graph, it reveals patterns, correlations, or trends, aiding in the identification of potential connections between factors. This image provides a quick and easy way to understand the relationships within a dataset.
Whether assessing cause-and-effect dynamics or identifying potential influencing factors, the Scatter Diagram is invaluable in understanding the interplay of variables and guiding strategic decision-making for effective problem-solving in diverse organizational contexts.
These tools collectively form a robust toolkit for organizations seeking to implement Root Cause Analysis effectively. Whether visualizing complex relationships with Fishbone Diagrams, probing deep with the 5 Whys, prioritizing efforts with Pareto Analysis, or anticipating failures with FMEA, each tool plays a unique role in the systematic identification and resolution of underlying issues, promoting a culture of continuous improvement within the organization.
Key Takeaways
The implementation of a root cause analysis method is pivotal for organizations aiming to address challenges effectively. Embracing structured approaches, such as brainstorming sessions and categorization, ensures a thorough examination of underlying issues.
To amplify these efforts, using AhaSlides for meetings and brainstorming sessions emerges as a game-changer. AhaSlides facilitates real-time collaboration, offering interactive tools for dynamic brainstorming and collective problem-solving. By leveraging AhaSlides, organizations not only streamline their root cause analysis processes but also foster an environment of engagement and innovation.
FAQs
What are the 5 steps of root cause analysis?
- Define the Problem: Clearly express the problem or issue for analysis.
- Collect Data: Compile pertinent data related to the problem.
- Identify Possible Causes: Brainstorm to generate a list of potential causes.
- Evaluate Causes: Analyze the identified causes, gauging their significance and relevance to the problem.
- Implement Solutions: Formulate and execute corrective actions based on the identified root causes. Monitor outcomes for sustained improvement.
What is the 5 Whys method?
The 5 Whys is a questioning technique used in root cause analysis to iteratively explore the cause-and-effect relationships behind a problem. The process involves asking "why" repeatedly, typically five times, to uncover deeper layers of causation until the fundamental root cause is identified.