Businesses and startups must regularly use a continuous improvement strategy to ensure their operations are efficient and effective. Therefore, if you are a leader or a business operator and want to learn how the constant improvement process can help your organisation, you will find answers in this article.
Overview
| When was the Continuous Improvement Examples Concept invented? | Masaaki Imai |
| When was Continuous Improvement Examples Concept invented? | 1989 |
| Where did continuous improvement originate? | Japan |
- The Concept of Continuous Improvement
- 4 Principles of Continuous Improvement
- 4 Continuous Improvement Methods
- 6 Tips & Examples of Continuous Improvement
- More on Leadership with AhaSlides
- Bottom line
- Frequently Asked Questions
The Concept of Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement process is a steady and continual process of making intentional changes to a company's business practices to improve process management, project management, and overall company operations.
Typically, the continuous improvement activities consist of a series of small changes that are stable day in and day out. Most continuous improvement activities focus on incremental, iterative improvements to the overall business process. In the long run, all these small changes can lead to a significant transformation.

Sometimes, however, continuous improvement can take bolder steps to upgrade the current state of the business, which especially applies to big events like new product launches.
4 Principles of Continuous Improvement
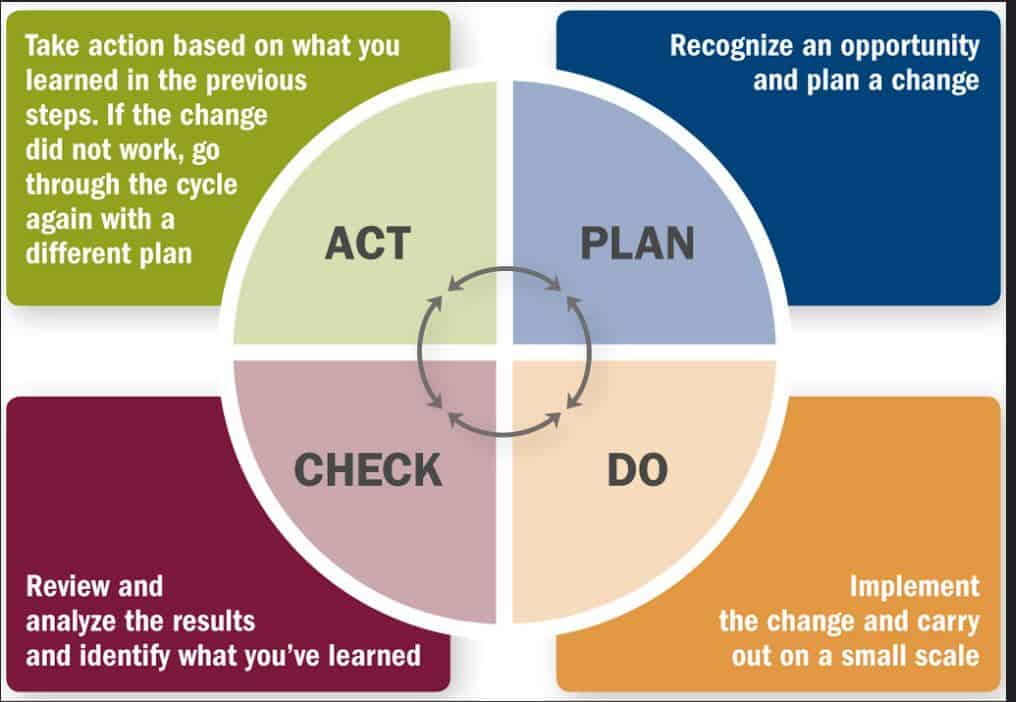
To implement the continuous improvement process, you need teamwork through the 4 Principles Plan - Do - Check - Act, also known as the PDCA cycle or Deming cycle:
Plan them first
This is the first and most important stage in the PDCA cycle. Accurate and complete planning will help guide the following activities. Planning includes defining objectives, tools, resources, and measures before going into specific production. Having conditions for more efficient exploitation of resources in the long term will contribute to reducing costs for quality management and improving competitiveness.
DO
Implement the program according to the plan established and reviewed in the previous stage.
When you've identified a potential solution, safely test it with a small-scale test project. It will indicate whether the proposed changes will achieve the desired results, with minimal risk of an undesirable outcome.
CHECK
Once the data collected from stage 2 is available, businesses have to regularly evaluate and check the overall performance of the improvement progress. This phase is necessary because it allows the company to evaluate its solution and modify the plan.
Evaluate performance with the following steps:
- Monitor, measure, analyse and evaluate customer satisfaction and collect data
- Organise internal audits
- Leaders re-evaluate
ACT
After standardising the stages above, the final step is to take action and adjust what needs improvement and what needs to be subtracted. Then, carry on the cycle of continuous improvement.
Four Continuous Improvement Methods
4 Continuous Improvement Methods, including (1) Kaizen, (2) The Agile Management Methodology, (3) Six Sigma and (4) Continuous Improvement and InnovationKaizen methodology
Kaizen, or rapidly improving processes, is often considered the "foundation" of all lean manufacturing methods. The Kaizen process focuses on eliminating waste, improving productivity, and achieving sustained, continual improvement in an organisation's target operations and processes.
Lean manufacturing was born based on the idea of kaizen. The team uses analytical techniques, such as value stream mapping and "5 reasons why" that work to implement the selected improvements (usually within 72 hours of starting the kaizen project) and often focuses on solutions that do not involve large capital expenditures.
The Agile Management Methodology
Agile methodology is a way to manage a project by dividing it into several phases. It is a process for managing a project that involves collaboration and continuous improvement at every stage.
Instead of a traditional project management approach, continuous improvement agile starts with an outline, delivering something in a short amount of time, and shaping requirements as the project moves forward.
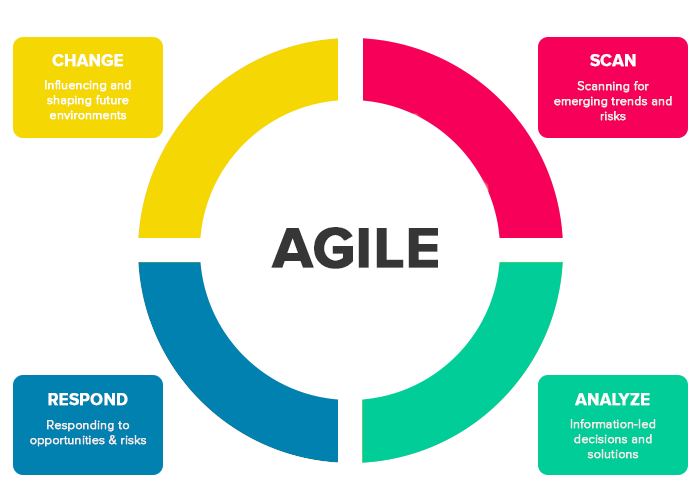
Agile is one of the most popular approaches to project management due to its flexibility, adaptability to change, and high level of customer input.
Six Sigma
Six Sigma (6 Sigma, or 6σ) is a system of business process improvement and quality management methods that rely on statistics to find defects, determine the causes, and resolve errors to increase process accuracy.
Six Sigma uses statistical methods to count the number of errors that arise in a process, then figure out how to fix it, bringing it as close to the "zero error" level as possible.
Continuous Improvement and Innovation
Continuous improvement and innovation, or CI&I, is a process that has been used to drive business improvement and innovation. It has eight steps that help business managers and employees focus on improving and innovating continuously, which will have the most impact on the goals of the business.
6 Tips & Continuous Improvement Examples
Developing Teamwork Skills
Continuous improvement requires the perfect and harmonious combination of members in an enterprise. Therefore, developing teamwork skills through team-building activities is indispensable. If members communicate and solve problems together well, the continuous improvement process will go smoothly.
For example, when a team is assigned an important task, they will know how to actively assign tasks such as who is the researcher, the contractor, and the presenter.
Improving Brainstorming
A helpful continuous improvement process always provides an opportunity for brainstorming sessions, which can help your team identify problems before they arise.
Here is an example: The sales director will ask the sales managers to hold monthly brainstorming sessions. Then the managers have separate brainstorming sessions with their team. This process will help the sales department identify areas for improvement and realise effective plans.

Receiving Feedback
Receiving feedback as well as complaining is an inevitable part of continuous improvement in the workplace. Let customers, employees, superiors, and even other teams review your team's work. This feedback will help your team figure out what your strengths and weaknesses are and what needs to be improved or omitted. You can use tools like SurveyMonkey or AhaSlides to get feedback quickly, anytime, anywhere.
For example, you use a single actor to do commercials for married products, which makes the customer feel that it is unreasonable and ask for a change.
Enhancing Quality Review
When collecting feedback, the team must always be ready to review its quality, such as time management quality, employee quality, product quality, and even leadership quality, for constant improvement to solve existing problems. These are also the high-performing teams that do it regularly. Here's an example:
A company suffers from reduced productivity due to excessive production time. So they decided to do an audit of their processes and operations to understand where the company was losing time. After this assessment, leaders had a better understanding of why productivity was low. As a result, they may implement new strategies or activities to optimise time as a resource.

Monthly Training
Along with developing teamwork skills, businesses and organisations should invest in their people. Need to train new professional skills monthly or take short courses to refresh their knowledge.
For example, A content writer every six months learns new skills, such as learning to write more movie scripts, learning to make short content on the latest platforms like TikTok or Instagram
Manage Potential Project Risks
Continuous improvement project management means that the project manager should conduct a risk management assessment throughout the life of the project. The sooner you can catch and deal with the risks to your project, the better. Do your review weekly or biweekly based on your team's delivery progress. If you are working on a big project that lasts six months, you can do it every two weeks. A 4-week short project needs more frequent checks.
For example, review the contract and payment progress of the partner regularly.
Bottom Line
The methods you use in your business create your own work culture. Many companies struggle to find the right direction by hiring better people, buying materials and machines at a lower cost, or even outsourcing or relocating their businesses to other countries. But in the end, only a continuous improvement approach and a culture of constant growth can help businesses establish a competitive advantage.
And never forget that to build a business with continuous improvement, focusing on team development is paramount. Be a great leader by creating a culture where each employee feels empowered to recognise inefficiencies and offer solutions. Create rewards or develop an accessible system for employees to share feedback continuously.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 6 stages of business?
The 6 stages of business: (1) Inception; (2) Planning; (3) Startup; (4) Profitability and Expansion; (5) Scaling and Culture; and (6) Business exit.
Which step of business process management allows managers to create a continually improving process?
Stage 5: Scaling and Culture.
What is continuous improvement?
Continuous improvement is an ongoing process of identifying, analysing, and making improvements to the current structure, to bring better performance towards individuals, teams and organisations.








