Ever get stuck in a rut, unable to see solutions outside your normal way of thinking?
Then you will definitely need to know the concept of divergent and convergent thinking.
Like Yin and Yang☯️, they work together harmoniously to help you get your ideas and solutions out effectively.
In this post, we'll break down exactly what these terms mean, and offer some tactics for incorporating more divergence into your process to unlock fresh perspectives and alternatives, followed by techniques for controlled convergence to judgment and decision.
Table of Contents
- Divergent and Convergent Thinking Explained
- Divergent and Convergent Thinking Examples
- Difference Between Divergent and Convergent Thinking
- How to Use Both Divergent and Convergent Thinking
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
Divergent and Convergent Thinking Explained
Divergent and convergent thinking are the terms coined by psychologist J.P. Guilford in 1956, referring to our thought processes when we need to come up with an idea for innovation, or a solution to a problem.
Divergent thinking is all about that wild, unrestricted ideation. It's the kind of thinking that encourages purely brainstorming without judgment.
When you're being divergent, you're thinking super broadly and letting all kinds of zany ideas flow freely. Don't censor anything - just put it all out there.
Convergent thinking is where those wild ideas start to narrow down. It's the analytical side that evaluates and refines the potential solutions.
With convergent thinking, you're narrowing down your options to what is most practical, viable or feasible. You start comparing ideas and fleshing them out more concretely.

To break it down simply: divergent thinking is breadth and exploration, while convergent thinking is depth and judgment.
Both are so important to have - you need that initial divergence to spark creativity and new possibilities. But you also need convergence to wrangle things into an actionable path forward.
🧠 Explore Divergent thinking in-depth in this article.
Divergent and Convergent Thinking Examples
Where do you see divergent and convergent thinking apply? Here are a few examples to help you have a better grasp of the importance of these thought processes in the daily tasks:
• Problem-solving at work: During a meeting to tackle a complex issue, the team first does a divergent brainstorming round - saying any ideas without critique. Then enters a convergent discussion to weigh the pros/cons of each, identify overlaps, and select the top few options to prototype.
Think beyond boundaries,
Explore limitless ideas with AhaSlides
AhaSlides' brainstorming feature helps teams to convert ideas into actions.
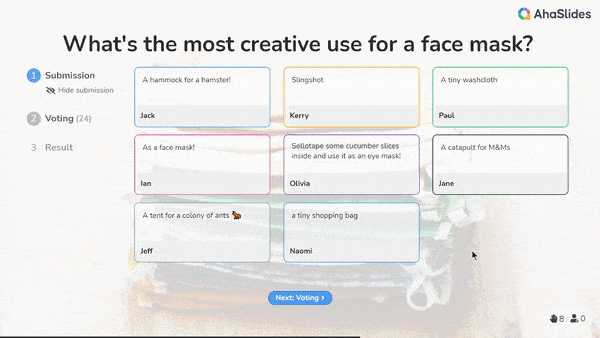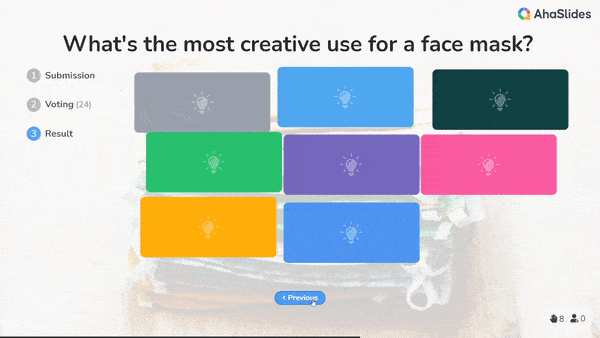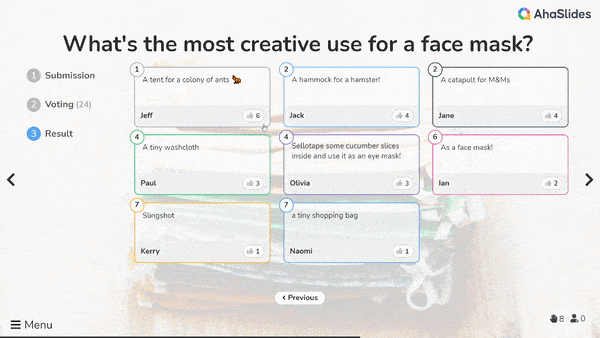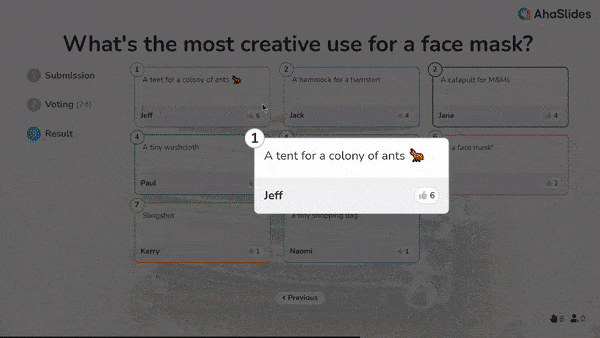
• Product design: In development, designers first divergently sketch a huge range of form/function concepts. Then convergently analyse which fulfills criteria best, combine elements, and refine one layout through iterative prototyping.
• Writing a paper: Initially free-writing and jotting any topics/arguments without censoring helps activate divergent thinking. Research then requires convergent focus, organising supporting evidence clearly under major themes.
• Planning an event: In the early stages, thinking divergently about potential themes, venues, and activities generates a pool of ideas. Organisers then convergently sift through factors like budget, timing, and popularity to select final details.
• Studying for a test: Divergently brainstorming all possible questions on flashcards gets topics into working memory. Then quizzing oneself convergently identifies weaknesses to focus extra review.
• Cooking a meal: Experimentally combining ingredients using divergent intuition leads to new recipes. Repeated convergent refinement helps perfect techniques and perfect flavours.
Difference Between Divergent and Convergent Thinking
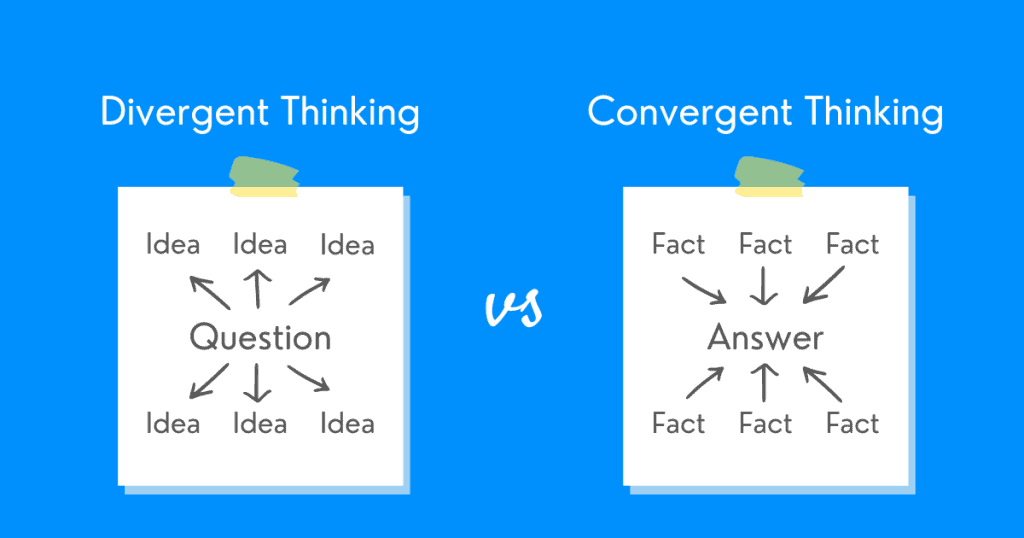
The main differences between convergent and divergent thinking are shown in the table below:
| Convergent Thinking | Divergent Thinking | |
| Focus | focuses on one best or correct answer or solution. | explores multiple answers or solutions that may be equally valid. |
| Direction | moves in one direction, evaluating ideas to arrive at a single conclusion. | branches out in many directions, making new connections between seemingly unrelated ideas. |
| Judgment | evaluates ideas and critiques them as they arise. | suspends judgment, allowing ideas to emerge without immediate evaluation. |
| Creativity | tends to rely on established procedures and previous knowledge. | stimulates novel, imaginative ideas through flexibility, playfulness and mixing categories/concepts. |
| Purpose | is used to refine ideas and arrive at a single best answer. | generates a variety of ideas at the exploration stage of problem-solving. |
| Examples | convergent activities are critique, evaluation, strategic planning, and troubleshooting. | divergent activities are brainstorming, hypothetical scenarios, mind mapping, and improvisation. |
How to Use Both Divergent and Convergent Thinking
Mastering a mixture of both thinking processes can be challenging, but we will guide you through each step to help fuel your journey from point A to point B.
#1. Discover (Divergent)

The goal of the Discover stage is divergent thinking and exploratory research to better understand learners.
Objective tools like field observations, interviews and reviewing existing materials are used to eliminate assumptions and avoid prematurely judging solutions.
You'll need to immerse in the learner environment and context to gather as much information as possible from multiple perspectives (learners, stakeholders, subject matter experts, and such).
Open-ended questions and active listening techniques help surface learner needs, challenges, preexisting knowledge and perspectives without bias.
The data collected informs but does not limit subsequent stages. Broad discovery aims to uncover nuances versus confirming hypotheses.
Findings from this stage are analysed at the Define stage rather than trying to interpret during information gathering.
The divergent, exploratory mindset of Discover helps develop an informed understanding of the learners and the situation.
#2.Define (Convergent)

The goal of this second stage is convergent thinking to analyse the output from the Discover stage and arrive at an actionable next step.
Tools like mind maps, decision trees, and affinity mapping are used to logically organise, sort and synthesise the qualitative discovery findings.
You then look for patterns, insights, and common themes across the raw data without any single data point being more important than another.
The convergent analysis aims to pinpoint the core issue based on learner needs/challenges rather than content areas or easy solutions.
You'll then have a well-defined problem statement that succinctly captures the learner's problem in objective terms and considers multiple perspectives.
Additional discovery may be needed if findings don't clearly indicate a problem or more research questions arise.
This Define stage sets the stage for developing solutions in the subsequent Develop stage, which marks the transition from problem-finding to problem-solving.
#3. Develop (Divergent)

The goal of the Develop stage is divergent thinking and broad brainstorming of potential solutions.
Your team will shift mindsets back to a more exploratory, creative mode without criticising ideas.
Your inputs include the problem statement defined in the previous stage to focus on brainstorming.
A facilitated brainstorming session which uses techniques like random stimulation can be used to spark new possibilities.
Everyone's ideas, no matter how crazy they are, should be encouraged to challenge assumptions.
Remember that you should think of quantity over quality at this stage to fuel the later Deliver stage.
Affinities can then begin forming between ideas at the edges without combining too soon.
It sets the solution foundation before converging on final recommendations in the Deliver stage.
#4. Deliver (Convergent)

The goal of the Deliver stage is convergent thinking to evaluate ideas and determine the optimal solution. It aims to maximise solution quality, impact and uptake based on a strategic thinking framework.
You can use tools like impact/effort matrices, and PICOS (Pros, Ideas, Cons, Opportunities, Strengths) criteria to structure the analysis and systematically review each potential solution based on pre-defined evaluation factors.
When you evaluate each factor, consider the relevance to the problem definition, feasibility, risks/challenges, and added value.
Early ideas may be recombined or modified based on evaluation insights.
With logical critiques, consensus-building and enough details for implementation, you will come up with the most fitted solution/recommendation.
Optional future explorations or next steps can also be identified.
Key Takeaways
Alternating between divergent and convergent thinking really helps you approach challenges from all angles.
The divergent parts get the creative juices flowing so you can consider lots of "what if" scenarios you'd normally miss while converging helps you actually assess what's realistic instead of getting lost in pipe dreams.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an example of divergent thinking?
An example of divergent thinking can be coming up with many fun punishments for the loser who lost the game.
What is divergent vs convergent vs lateral thinking?
When it comes to sparking creativity, divergent thinking is your best friend. It encourages freely exploring any and all ideas that pop into your head without any criticism. But coming up with wild concepts is only half the battle - it's time to put on your analytical skills. Convergent thinking is about logically picking apart each possibility to find the actual diamond in the rough. Sometimes though, you gotta say "screw the rules" and let your thoughts wander to uncharted territories. That's where lateral thinking shines - it's about making connections in ways that would never occur to more linear thinkers.